Students can read the important questions given below for Resources Mobilization Class 12 Entrepreneurship. All Resources Mobilization Class 12 Notes and questions with solutions have been prepared based on the latest syllabus and examination guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS. You should read all notes provided by us and Class 12 Entrepreneurship Important Questions provided for all chapters to get better marks in examinations. Entrepreneurship Question Bank Class 12 is available on our website for free download in PDF.
Important Questions of Resources Mobilization Class 12 Entrepreneurship
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: What do you understand by internal sources of finance?
Answer: Internal sources of finance is referred to as owner’s own money. It is also known as owner’s equity. Particularly in the case of small entrepreneurs the owner’s money is very small.
Question:‘Production’, ‘Marketing’, and Financing’ – deemed as the most important factors for any business’s survival rates. Among these name the most critical element and why?
Answer: Production, marketing, and financing, deemed to be the most important factors for any business survival. ‘ Financing’ is considered to be the first because no entrepreneur can start and run the business without money. Among this the most critical element for success in business is ‘Finance’. Before doing anything, an entrepreneur should clearly answer the following three questions:
1. How much money is required?
2. Where will money come from?
3. When does the money need to be available?
3. Name the most important prerequisite to start an enterprise.
Answer: Finance is the most important prerequisite to start an enterprise.
Question: How will you differentiate between financial market with other market? Give one difference.
Answer: Financial market is a market in which people and entities can trade financial securities (stocks and bonds), commodities (including precious metals or agricultural goods), and others like crude oil etc. at prices that reflect supply and demand. Market refers to the aggregate of possible buyers and sellers of a certain good or service and the transactions between them.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Question: Name the sources of demand for capital comes from.
Answer: Capital market consists of lenders and borrowers:
1. Lenders supply the funds
2. Investors demand the funds The demand for capital comes from:
1. Industrial Sector – It comes from the private sector into manufacturing or other economic activities.
2. Government
Question: Which sources provide the supply for long-term funds?
Answer: Capital market consists of lenders and borrowers: Lenders supply the funds. Investors demand the funds. The supply of long-term funds comes from following sources:
1. Household savings
2. Foreign capital
3. Institutional investors
4. Corporate savings
5. The government
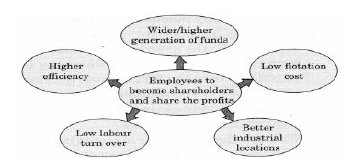
5. How stock options lead to enable employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company?
Answer: Stock options or offering shares to the employees has gained much popularity in many countries of the world. This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company leading to:
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: Define capital market.
Answer: A capital market may be defined as an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital or financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs.
Question: Identify the method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
Answer: Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
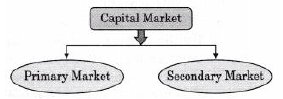
Question: Name the two players in the capital market.
Answer:
Question: Identify the reward IPO investors seek as an appreciation of their investment.
Answer: The only reward the IPO investors seek is an appreciation of their investment and possibly dividends.
Question: What do you understand by pro-rata allotment of securities?
Answer: It is used to describe a proportionate allocation. It is a method of assigning shareholders a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: State the nature of money market. Who are the major participants in the money market?
Answer: Money market refers to transactions involving lending and borrowing of money for short periods like a day a week a month or 3 to 6 months. It meets the short term requirements. The major participants in the market are:
1. Reserve Bank of India
2. Commercial Banks, Cooperative Banks
3. Non-Banking Finance Companies
4. State Government
5. Large Corporate Houses and Mutual Funds
6. LIC, GIC, UTI, etc.
Question: Write down the sectors of organized and unorganized market.
Answer: The capital market in India may be broadly classified into:
A. Organized Markets: This segment comprises of
1. Corporate enterprises
2. Government and semi-government institutions requiring funds for various development activities
3. Individual investors
4. Corporate and institutional investors, as LIC, Banks, Finance Corporations, International financing agencies, etc.
B. Unorganized Sector:
The unorganized sector consists of
1. The indigenous bankers in urban areas.
2. The money lenders in rural areas.
5. What is meant by primary market? Briefly explain the concept of ‘Right Issue for existing companies’.
Answer: Primary market is basically meant to facilitate transfer of resources from the savers to the entrepreneurs seeking funds for:
1. Setting new enterprises,
2. Expanding,
3. Diversifying.
1. Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
2. It is proposed through a circular to all the existing shareholders only.
3. It is not mandatory to purchase these shares if any shareholders are not willing to subscribe, they can reject or disclaim and others can subscribe for it.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: What are the responsibilities of governing body?
Answer: The governing body is responsible for policy formulation and proper functioning of the exchange, having wide range of powers:
1. Elect the office bearers and set up committees
2. Interpret rules, regulations and by-laws
3. Admit and expel members
4. Adjudicate disputes
5. Manage the properties and finance of the exchange
6. Conduct the affairs of the exchange.
Question: Name the stock exchanges where most of the stock trading in India is done.
Answer: Most of the stock trading in India is done on NSE and BSE. The BSE is the Bombay Stock Exchange and the NSE is the National Stock Exchange. The BSE is situated at Bombay and the NSE is situated at Delhi. These are the major stock exchanges in the country.
Question: What is a secondary capital market?
Answer: Any transaction in shares or debentures subsequent to its primary offering is called “Secondary Transaction”. Thus, the secondary capital market, which is also known as old securities market or stock exchange deals- with buying and selling of old securities i.e. the market securities issued earlier are sold by existing investors in this market.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION
Question: What is the alternate name of stock used by different people?
Answer: The word “stock” is called by different names with different people like shares, equity, scrip and so on but all these words have same meaning.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: Explain the importance of Stock Exchange from the viewpoint of society.
Answer: From the societies point of view:
1. Rapid Capital Formation
2. Economic Development
3. National Projects
Question: Rahil (Finance) and Anushk (HR) are doing MBA (IIM Indore). While reading the newspaper Anushk saw the heading Sensex goes up. But last week the heading was different that Sensex goes down now some confusion was going on her mind, immediately she asked her Friend Rahil the same? Now according to you how Rahil will clear the confusion of Anushk? Explain and give some value points.
Answer: Rahil explains him in this way: The Sensex is an “index”. An index is basically an indicator. It gives you a general idea about whether most of the stocks have gone up or most of the stocks have gone down. The Sensex is an indicator of all the major listed companies of the BSE. The BSE, is the Bombay Stock Exchange and the NSE is the National Stock Exchange. The BSE is situated at Bombay and the NSE is situated at Delhi. These are the major stock exchanges in the country. If the Sensex goes up, it indicates that the prices of the stocks (shares) of most of the major companies on the BSE have gone up. If the Sensex goes down, this tells you that the stock price of most of the major stocks on the BSE have gone down. In this way Rahil cleared the confusion of Anushk.
Value Points:
1. Quest for knowledge
2. Helpfulness
3. Consideration for others
4. Awareness of responsibility
5. Readiness to cooperate
6. Friendship.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: Who manages SEBI?
Answer: SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of following:
1. Chairman who is nominated by Union Government of India.
2. Two members, i.e. Officers from Union Finance Ministry.
3. One member from Reserve Bank of India.
4. The remaining 5 members are nominated by Union Government of India, out of them at least 3 shall be whole-time members.
Question: Explain briefly the three functions of SEBI rolled into one body.
Answer: SEBI has quasi-legislative capacity as it makes rules and regulations. It has rule-making authority related to the matters of securities in India.
SEBI is a quasi-judicial body as it has an entity such as an arbitrator or tribunal board, and has powers and procedures resembling those of a court. SEBI is quasi-executive as it functions like an executive but that is not really an executive.
Question: What is SEBI and what is its role?
Answer: The Securities and Exchange Board of India or SEBI is the regulator for the securities market in India. Role of SEBI:
1. It is a supervising and regulatory body to check certain malpractices and works for promoting the securities markets in India.
2. It has three functions rolled into one body: quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial and quasiexecutive.
3. It drafts regulations in its legislative capacity, it conducts investigation and enforcement action in its executive function and it passes rulings and orders.
Question: Enlist several categories of financing possibilities in which smaller ventures sometimes rely on.
Answer: Following are several categories of financing possibilities in which smaller ventures sometimes rely on:
1. Venture capital
2. Seed Capital Finance
3. Start up finance
4. Loan from various financial institutions like, IDBI, SIDBI, IFCI, ICICI, NABARD, IIBI, SFCs, TFCI, AND SIDC.
HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Question: Why it is said that “A venture capitalists investments are illiquid”. Give reason.
Answer: Illiquid describes an asset or security that cannot be sold quickly. Uncertainly the asset value is associated with the investment. This can be due to economic instability or issues relating to the asset. If the asset value declines, it becomes an illiquid asset due to the unclear value. It can be hard to locate a market for these products. This may lead to loss of the money.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: Write a short note on IIBI.
Answer: Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI): The Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was formed by transforming the Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI). It was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies. IRBI was incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 and renamed as the Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. in March 1997. Functions: IIBI offers a wide range of products and services such as:
1. Term-loan assistance for project finance
2. Short duration non-project asset – backed financing working capital/ other short term loans to companies
3. Equity Subscription Asset Credit
4. Equipment finance
5. Investments in Capital Market and Money market instruments.
Question: Describe the form of assistance provided by SIDBI to the industrial concern.
Answer: The financial assistance of SIDBI to the small scale sector is channelised through the following two routes:
1. Indirect Assistance: Under its indirect schemes, SIDBI extends refinance of loans to small scale sector by Primary Lending Institutions (PLIs) viz. SFCs, SIDCs and Banks. At present, such refinance assistance is extended to 892 PLIs and these PLIs extend credit through a net work of more than 65,000 branches all over the country. All the Schemes of SIDBI both direct and indirect assistance are in operation in all the States of the country through 39 regional/branch offices of SIDBI.
2. Direct Assistance: SIDBI directly assists SSIs under:
o Project Finance Scheme
o Equipment Finance Scheme
o Marketing Scheme
o Vendor Development Scheme
o Infrastructural Development Scheme
o ISO-9000
o Technology Development & Modernisation Fund.
VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: Explain in detail objectives and three important Primary functions of NABARD.
Answer: National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD): On 15th December, 1981, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) Bill was passed in the Parliament, which started functioning on 1st July, 1982. NABARD was established according to the Preamble to the Act, for providing credit for the promotion of:
1. Agriculture
2. Small-scale Industries
3. Cottage and Village Industries
4. Handicrafts and other rural crafts
5. Other economic activities in rural areas with a view for promoting IRDP.
Objectives:
1. The bank will serve as a financing institution for institutional credit such as long-term, short-term, and for the promotion of activities in rural areas.
2. To provide direct lending to any institution as may be approved by the central government.
Functions: The primary functions of NABARD can be classified under three heads:
1. Credit Functions: NABARD provides different types of refinance to eligible institutions. They assist entrepreneurs through:Short-term credit to State Cooperative Banks, Regional Rural Banks and Other financial institutions approved by RBI.
2. Developmental Functions:
o NABARD coordinates the operations of rural credit institutions.
o It develops expertise to deal with agricultural and rural problems so as to assist in rural development efforts.
3. Regulatory Functions:
o NABARD is empowered to undertake inspection of RRBs and Cooperative Banks, other than the Primary Cooperative Banks.
o Toopenanew branch, arecommendation ofNABARD is imperative by RRBs or Cooperative Banks to seek permission from RBI.
Q1. Explain the main objectives and functions of ICICI.
Answer: The ICICI has been established to achieve the following objectives:
HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Question: Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of financial institutions for an entrepreneur.
Answer: Advantages of financial institutions for an entrepreneur:
1. Borrowing money from the bank is one of the simplest ways to get needed funds to start or grow your business.
2. To grant loans and advances.
3. To underwrite or to subscribe to shares or debentures of industrial concerns.
4. To guarantee loans raised by industrial concerns in the market.
5. To provide consultancy and merchant banking services in or outside India.
6. To provide technical, legal, marketing and administrative assistance to any industrial concern or person for promotion, management or expansion of any industry.
7. Co-ordination, regulation and supervision of the working of other financial institutions such as IFCI, ICICI.
8. To act as trustee for the holders of debentures or other securities.
9. To provide long and medium-term credit to industrial concerns engaged in manufacturing, mining, shipping and electricity generation and distribution.
10. The bank will serve as a financing institution for institutional credit such as long-term, short-term, and for the promotion of activities in rural areas.
11. Provides financial assistance to enterprises for setting up or the development of tourism-related projects.
Disadvantages:
Procurement of finance involves risk and formalities to comply:
1. State Financial Corporations only provide long and medium-term loan repayment ordinarily within a period not exceeding 20 years.
2. Some financial institutions provide financial assistance generally to those industrial concerns whose paid up share capital and free reserves do not exceed Rs 3 crore.
3. Rate of interest is too high sometimes not able to pay the debt amount and its interest.
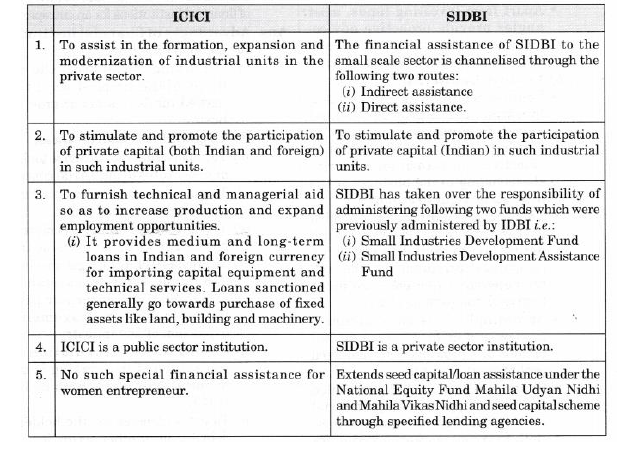
Question: Distinguish between ICICI and SIDBI.
Answer:
Question: Company A goes for public issue of 10,000 shares @ Rs 10 each. Application were received for only 5,000 shares. Can the company proceed with the process of issuing shares?
Answer: In the case of Company
A Issued shares to public — 10,000 Shares @ 10 each.
Applied share public by — 5,000 Shares @ 10 each.
Company receives only 50% of the subscription within 120 days from the date of the issue, then it is called as Minimum subscription. As per the SEBI guidelines, if the company does not receive 90% of the issue amount from the public subscription including development from underwriters within 120 days from the date of the issue, the amount of subscription received is required to be refunded to the applications. In case of disputed development also, subscription is required to be refunded if 90% of the issued amount plus accepted. Development from underwriters if any is not received within 120 days of the issue of prospectus, all the money received from the applicants for shares is required to be repaid forthwith without interest and if any such money is not so repaid in the next 10 days (after the expiry of 120 days), the directors of the company are jointly and severally liable to repay that money, with interest from the expiry of the 130 days. The company should refund the amount within 10 weeks of the closing of the subscription list and pay interest, if refunds are delayed by more than 8 days after this period.
Question: How NABARD is different from TFCI?
Answer:

VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Identify the logo given below.
Answer: IDBI Bank.

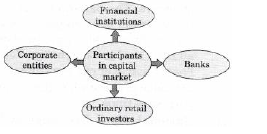
Question. List any four participants in capital market.
Answer:
Question. Name one financial institution which was formed by transforming The Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India.
Answer: The Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was formed by transforming The Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI).
Question. Name one of the financial institutions guaranteeing loans raised by Industrial concerns which are repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
Answer: State Financial Corporations (SFCs) guaranteeing loans raised by industrial concerns which are repayable within a period not exceeding 20 years.
Question. Name one financial institution which can sanction amount to a single concern i.e. minimum amount Rs. 5 lakhs and it does not go beyond the maximum limit of Rupees one crore.
Answer: Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI).
Question. What do you mean by “Financial Intermediation”?
Answer: The role of transferring financial resources from the surplus units to the deficit units is referred to as “Financial Intermediation”.
Question. Name one financial institution which extends seed capital/loan assistance under the National Equity Fund, Mahila Udyan Nidhi and Mahila Vikas Nidhi.
Answer: Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI).
Question. Name one financial institution which was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies.
Answer: Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI) was set up by IDBI at the instance of the Government of India in April 1971 for rehabilitation of sick industrial companies.
Question. Why stock exchange is called as the ‘financial barometers’ and development indicators of national economy?
Answer: Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country. Industrial growth and stability is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
Question.Who plays a very vital role in a financial intermediatary.
Answer: Capital markets play a very vital role in a financial intermediatary.
Question. By which act the organisation, management, membership and functioning of stock exchanges in India are governed?
Answer: The organisation, management, membership and functioning of stock exchanges in India are governed by the provisions of The Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956.
Question 14. Who are in need of the help of capital markets?
Answer: The help of capital market is for:
1. Industry
2. Trade
3. Finance
4. Government.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question.“ Stock market imparts liquidity to investment.” Comment.
Answer:
1. “Stock market imparts liquidity to investment.’’The important function of stock market is to provide a ready and continuous market for the sale and purchase of securities.
2. It also gives an investor to reinvest and disinvest.
3. This market imparts liquidity to the long-term securities held by them by providing an auction market for these securities.
4. It enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
Question. Mohit Pipes and Tube Co. Ltd. goes for public issue of 10,000 shares @ Rs 10 each. Applications were received for 15,000 shares. How did the company proceed with the process of issuing shares?
Answer: In the case of Mohit Pipes and Tube Co. Ltd Issued shares to public — 10,000 Shares @ 10 each. Applied share public by — 55,000 Shares @ 10 each. Company receives only 150% of the subscription within 120 days from the date of the issue, it is called as Over-subscription. Company will proceed with the issued shares i.e. 10,000 shares and excess shares will be refunded according to SEBI guidelines. The over-subscribed amount after the finalisation of allotment, should be refunded to the applicants within 10 weeks of the closure of subscription list. If the money is not so refunded, the company is liable to refund the money with interest as specified from the expiry of the 8 days after 10 weeks of the closure of subscription list.
Question.For what type of ventures SIDBI provide Venture Capital assistance to the entrepreneurs.”
Answer: SIDBI provide venture capital assistance to the entrepreneurs for their innovative ventures if they have a sound management team, long term competitive advantage.
Question. How venture capital can best be characterized as a long-term investment discipline?
Answer: Venture capital can best be characterized as a long-term investment discipline, usually occurring over a five-year period that helps in the creation of
1. early-stage companies,
2. the expansion and revitalization of existing businesses, and
3. the financing of leveraged buyouts of existing divisions of major or privately owned enterprises.
Question. Name some Institutional investors to whom entrepreneurs can raise funds by selling the issues.
Answer: Entrepreneurs, herein, raise funds by selling the issues mainly to the institutional investors like:
1. Unit Trust of India
2. Life Insurance Corporation of India
3. General Insurance Corporation of India
4. Army Group Insurance
5. State Level Financial Corporations, etc.
Question. How the prices of different securities traded are shown in the stock market?
Answer: The price of different securities traded are shown on electronic boards.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. What do you understand by Public Issue/ Going Public/Offers Through Prospectus/ Initial Public Offers (IPOs)?
Answer: Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus.
1. It involves all public limited company can raise the required funds
commonly by preparing a prospectus.
2. Prospectus helps a company to raise funds through public.
3. When an entrepreneur offers shares to the public for subscription he/she is required to comply with all the restrictions and formalities according to the provision of companies Act and SEBI Guidelines of pertaining to the initial issues, prospectus drafting and launch 4. The issues must be listed on at least one stock exchange.
Question. “ Stock exchanges are the financial barometers of an economy”. How?
Answer:
1. Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country.
2. It help businesses to raise capital and give investors opportunities to back new and established enterprises.
3. It also help business and entrepreneurs to come together to buy and sell trade shares for the purpose to raise more capital.
4. Continuous growth of industries is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
5. Rising stock market, through rising prices, more investors can create asense of confidence and gives positive direction in the growth of an economy.
Question. Why is stock exchange important for an investor?
Answer: Importance of stock exchange from the viewpoint of investors:
1. Dissemination of useful information: Stock exchange publishes useful information regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals. The interested persons buy and sell their securities on the basis of information provided by the stock exchanges.
2. Ready market: Persons desirous of converting their shares into cash may easily do so through a member of stock exchange.
3. Investors’ interests protected:Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not exploit the investors.
4. Genuine guidance about the securities listed: The investors can safely depend upon the information provided by the stock exchanges.
5. Barriers of distance removed: Stock exchange removes the barriers of distance with regard to securities listed there. Without stock exchange the securities of a Delhi company may have a limited market in Delhi only.
6. Knowledge of profit or loss on investments: The investors canestimate the profit or loss on the total amount of investments in securities, by comparing the original amount invested and the price of securities on a particular day.
Question. Ram was very thrilled with his new job. He was placed in a small factory manufacturing door knobs as a stock keeper. After a few days, while taking stock he understood that nuts and various small parts constituted majority of the cost of production. After some time, the firm went into a loss and the owner decided to look into the various factors that could have constituted the loss. Ram expressed his concern that inventory was not properly maintained and that there are various techniques which are involved and if followed properly the company will not be in a loss. The owner agreed to the suggestion. He also decided to take help from some specialized government institution initiate steps for technological up gradation, and modernization of existing units.
1. What technique was suggested by Ram? Explain it.
2. Which specialized financial institution is the owner thinking of approaching and state any one of its objectives?
Answer:
ABC Analysis:
1. The inventory control technique known as ABC analysis builds on Pareto’s Principle. In ABC analysis, a company reviews its inventory and sorts all SKUs into three categories, called ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ items. The typical breakdown might look like this: ‘A’ inventory: 20 per cent of SKUs, 80 per cent of value. ‘B’ inventory: 30 per cent of SKUs, 15 per cent of value. ‘C’ inventory: 50 per cent of SKUs, 5 per cent of value. A particular company’s numbers may be different, hut the pattern would be similar we should be able to discern a similar kind of pattern.
2. SIDBI (Small Industries Development Bank of India) Objectives of SIDBI are:Initiate steps for technological up gradation, and/or modernization of existing units.
VERY LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Who are called as “Angel Investors”? Explain the features of “Angel Investors”.
Answer: Business angel or informal investor or an angel investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start¬up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
Features of Angel Investors: Providing start-up finance to the needy who want to start a small own business. The main people involved to provide funds are “friends and family”, (it can be seed funding and formal venture capital). But raising of funds cannot be more than a few thousands from friends and family, even the venture capitalist are least interested to make investments. Thus, angel investments is a common second round of financing for high-growth start-ups or early stage companies.
1. Most angel investors are current or retired executives, business owners or high net worth individuals who have the knowledge, expertise, and funds that help start-ups match up to industry standards.
2. They bear extremely high risk and are usually subject to dilution from future investment rounds.
3. They expect a very high return on investment.
4. Apart from investing funds, most angels provide proactive advice, guidance, industry connections and mentoring start-ups in its early days.
5. Their objective is to create great companies by providing value creation, and simultaneously helping investors realize a high return on investments.
6. They have a sharp inclination to keep abreast of current developments in a particular business arena, mentoring another generation of entrepreneurs by making use of their vast experience.
Question. “Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs.” Explain its benefit and drawbacks.
Answer: Meaning of Public Issues: This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. When an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company, he/ she tends to be in advantageous position because of reaping the following benefits: Access to capital or raising funds:
1. An entrepreneur stands to gain by going public in access to capital.
2. Generally, the capital is paid off at the liquidation of a company or not to be repaid immediately and does not involve an interest charge.
3. The only reward the IPO investors seek is an appreciation of their investment by getting dividends.
Entrepreneur can use the capital raised for a variety of purposes including:
1. growth and expansion,
2. retiring existing debt,
3. corporate marketing and development,
4. acquisition capital.
Other advantages:
1. Mergers and acquisitions: Public stock of a company can be used for businesses to grow through acquisitions.
2. Higher valuations: Public companies are typically valued more than private companies.
3. Benchmark trading price: The trading price of a public company’s stock serves as a benchmark of the offer price of other securities.
4. Capital formation: Raising capital later is typically easier because of the extra liquidity for the investors.
5. Incentives: Stock options and stock incentives can be very helpful in attracting employees.
6. Reduced business requirements: While an underwritten initial public offering requires significant earnings, the lack of earnings does not keep a private company from going public.
7. Less dilution: There is less dilution of ownership control compared to an IPO.
8. Liquidity: A public company provides liquidity for management, minority shareholders, and investors.
9. Prestige: Added prestige and visibility with customers, suppliers, as well as the financial community.
Question. Explain the features of Stock Exchanges.
Answer: Following are the features of stock exchange—:
1. Association of persons: It is an association of persons or body of individuals which may be registered or unregistered.
2. Recognition from central government: It is an organized market. It requires recognition from the Central Government.
3. Market for securities: It is a market, where securities of corporate bodies, government and semi-government bodies are bought and sold.
4. Deals in second hand securities: It deals with shares, debenture, bonds and such securities already issued by the companies. In short, it deals with existing or second hand securities and hence it is called secondary market.
5. Regulates trade in securities: It does not buy or sell any securities on its own account. It merely provides the necessary infrastructure and facilities to its members and brokers who trade in securities. It regulates the trade activities so as to ensure free and fair trade.
6. Allow dealings only in listed securities: It always maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on its floor.
7. Transactions effected only through members: All the transactions in securities at the stock exchange are effected only through its authorized brokers and members. No outsiders or direct investors are allowed to enter in the trading circles of the stock exchange.
8. Working as per rules: Buying and selling transactions in securities at the stock exchange are governed by the rules and regulations of stock exchange as well as SEBI Guidelines. No deviation from the rules and guidelines is allowed in any case.
9. Specific location: It is a particular market place where authorized brokers come together daily (i.e. on working days) on the floor of market called trading circles and conduct trading activities. The price of different securities traded are shown on electronic boards. After the working hours market is closed. All the working of stock exchange is conducted and controlled through computers and electronic system.
10. Financial barometers: Stock exchanges are the financial barometers and development indicators of national economy of the country. Industrial growth and stability is reflected in the index of stock exchange.
Question. When was SEBI established? What are the main aims of SEBI?
Answer: 1.SEBI was officially established by The Government of India in the year 1988 and given statutory powers in 1992 with SEBI Act, 1992 being passed by the Indian Parliament.
2. SEBI has it’s Headquarter at the business district of Bandra Kurla Complex in Mumbai, and has Northem, Eastern, Southern and Western Regional Offices in New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai and Ahmedabad respectively.
3. Initially, SEBI was a non-statutory body without any statutory power. However, in the year of 1995, SEBI was given additional statutory powers by the Government of India through an amendment to the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992. In April, 1998 the SEBI was constituted as the regulator of capital markets in India under a resolution-of the Government of India. SEBI’s Establishment: SEBI was established as a supervising and regulatory body to curb certain malpractices and to promote the Securities Markets in India.
Question. When and how to seek Venture Capital Finance?
Answer: Entrepreneurs can typically seek venture capital to assist at any of the following four stages in the company’s development:
(i) Early stage financing this stage includes:
(a) Seed capital
(b) Pre-start up and start up
(c) Second-round financing
(a) Seed capital finance:
• It refers to the capital required by an entrepreneur for conducting research at pre-commercialization stage.
• During this stage, the entrepreneur has to convince the investor (VC) why his idea/product is worthwhile.
• The investor will investigate into the technical and the economical feasibility of the idea.
• In some cases, there is some.sort of prototype of the idea/product that is not fully developed or tested.
• As the risk element at this stage is very high, investor (VC) may deny to assist if he does not see any potential in the idea.
• Entrepreneur’s ability, technological skills and competencies are required to match with the market opportunities so as to successfully convince about product/idea’s feasibility to the venture capitalist.
(b) Start up finance:•
If the idea/product/process is qualified for further investigation and/or investment, the process will go to the second stage; this is also called the start-up stage.
• A business plan is presented by the entrepreneur to the VC firm. A management team is being formed to run the venture.
• If the company has a board of directors, a person from the VC firms will take seats at the board of directors.
• While the organisation is being set up, the idea/product gets its form.
• The prototype is being developed and fully tested.
• Sometimes, clients are being attracted for initial sales. The management-team stablishes a feasible production line to produce the product.
• The VC firm monitors the feasibility of the product and the capability of the management-team from the board of directors.
(c) Second-round financing:
• At this stage, the time comes the idea has been transformed into a product and is being produced and sold.
• This is the first encounter with the rest of the market, the competitors and attempt is to squeeze in the market and get some market share from the competitors.
• The entrepreneur, at this stage, needs assistance from the Venture Capitalist for expansion, modernization, diversification so that the economies of scale and stability could be attained.
(ii) Last stage financing/bridge/pre-public stage: In general, this is the last stage of the venture capital financing process. The main goal of this stage is for the venture to go public so that investors can exit the venture with a profit commensurate with the risk they have taken. At this stage, the venture achieves a certain amount of market share. This gives the venture some opportunities for example:
• Merger with other companies.
• Keeping new competitors away from the market.
• Eliminate competitors.
• Development capital.
Question. State the limitations of Public Issues.
Answer: The various limitations/obligations’ are as follows:
1. Increasing accountability to public shareholders.
2. Need to maintain dividend and profit growth trends.
3. Becoming more vulnerable to an unwelcome takeover.
4. Need to observe and adhere strictly to the rules and regulations by governing bodies.
5. Increasing costs in complying with higher level of reporting requirements.
6. Relinquishing some control of the company following the public offering.
7. Suffering a loss of privacy as a result of media interest.
VALUE BASED QUESTIONS
Question. Explain the importance of a stock exchange from the view point of entrepreneurs/companies.
Answer: The importance of a stock exchange from the view point of entrepreneurs /companies:
1. Recognition: The market values of companies’ shares are published in important dailies. This enhances the reputation of good companies/ entrepreneurs.
2. Wide market: The securities of some companies are listed in some stock exchanges. The market for the securities of such companies is considerably widened. Thus, larger amounts of capital may be raised from different types of investors.
3. Higher share values: People have a tendency to buy shares that have some premium value. Demand of such shares increases. This leads to further increase in the price of such shares.
Value Points:
• Enhances the reputation of good companies
• Universal
• Social services
• National awareness
• Readiness to cooperate
• Helpfulness
• Consideration for others
• Friendship
Question. Explain the importance of a stock exchange from the viewpoint of investors.
Answer: From the viewpoint of investors
1. Dissemination of useful information:
(?) Stock exchange publishes useful information regarding price lists, quotations, etc., of securities through newspapers and journals.
(b) All the shareholders who wish to buy and sell their securities accordingly use the provided information.
2. Ready market: It gives a ready market for the security holders, so that all those who wish and are in need of money can easily convert their shares into cash online or through intermediaries. –
3. Investors’ interests protected: Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations so that members may not exploit the investors.
4. Genuine guidance about the securities listed: The investors can safely depend upon the information provided by the stock exchanges.
5. Barriers of distance removed:
(a) Stock exchange removes the barriers of distance with regard to securities listed there. (b) Without listing the shares in stock exchange the securities can be sold out in a limited market only.
6. Knowledge of profit or loss on investments: The investors can estimate the profit or loss on the total amount of investments in securities, by comparing the original amount invested and the price of securities on a particular day.
Value points:
1. Sharing the information
2. Helpfulness
3. Quest for knowledge
4. Discipline in following rules and regulations
5. Resourcefulness
6. Equality for all regarding the brokerage
7. Team spirit
8. Universal
9. Shareholders shows the spirit of enquiry.
Question. “ Stock market contributes to better allocation of capital and intensities capital formation.” Do you agree? Explain.
Answer: Yes, I agree with the statement. Stock market contributes to better allocation of capital and intensifies capital formation. The shares of profit making companies are quoted at higher prices and are actively traded so such companies can easily raise fresh capital from stock market. The general public hesitates to invest in securities of loss making companies. So stock exchange facilitates allocation of investor’s fund to profitable channels. Stock exchange intensifies the process of capital formation through creating the habit of saving, investing and risk taking among the investing class by converting their savings into profitable, safe investments.
Question. Explain the importance of a stock exchange from the viewpoint of society.
Answer: The importance of a stock exchange from the viewpoint of society:
1. Rapid capital formation:
(a) Many people save their money and are ready to invest where they can get high rate of returns, when they check with the good companies with high premium amount they tempted to invest in securities.
(b) This habit leads to investment of savings in corporate and government securities.
(c) The high returns of dividend from these securities may further be invested in buying more securities.
(d) This flow of funds leads to rapid and continuous capital formation.
2. Economic development:
(a) It is the market in which existing securities are purchased and sold.
(b) This process is called as disinvestment and reinvestment.
(c) Through easy funds mobilisation, this leads to more capital, enhancing economic development of the country.
3. National projects: As stock exchange promotes, the capital formation by rating and approving the projects which brings national prosperity can be easily undertaken.
Value Points:
1. National prosperity.
2. This habit leads to investment of savings in corporate and government securities.
3. Easy funds mobilizing.
4. Enhancing economic development.
5. Promoting the people to come with the projects.
6. Helping and providing the people a platform to buy and sell the securities.
7. Readiness to cooperate.
Question. Explain the necessity of a stock exchange in the economy.
Answer: Stock exchange indicates about the good or bad health of an economy. For the smooth and orderly functioning of corporate sector in a free market economy, stock exchanges are indispensable, because of the different roles played by them for different groups.
1. Stock exchange indicates about the good or bad health of an economy. It is an investment intermediary which facilitates economic and industrial development of a country.
2. All the stock markets influence economic activities through the creation of liquidity.
3. It increases the business and earnings of people and gives a positive impact to the growth of an economy.
4. Stock exchanges formulate rules and regulations and build a trust between the members and investors so that members may net exploit the investors, with this belief more number of investors are added into it, which is really helpful for the economic growth.
5. Through easy funds mobilizing, the boosted production fetches more capital, enhancing economic development.
6. It operates through the medium of stock exchanges which regulates the trading activities in this market and ensures a measure of safety and fair dealings to the investors.
7. Stock exchanges play a key role in allocating capital to the corporate sector, which has significant effects on the economy as a whole.
8. Stock exchanges maintain an official list of securities that could be purchased and sold on its floor. In entrepreneurial- oriented countries, the growth of listed companies contributes a wide portion of a nation’s increase in GDP.
9. Stock exchange provides a central market for purchase and sale of securities. It provides ready and continuous outlet for buying and selling of securities. Buyers and sellers strongly believe that they would be able to buy and sell securities as and when they want.


