Please refer to Waste Water Management Class 7 Science notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Science books for Class 7. You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 7 Science Waste Water Management Notes and Questions
WASTE
Any material which cannot be used in the form in which it is produced is called a waste. According to their physical state, waste can be classified into 3 categories – Solid waste, liquid waste & gaseous waste. The impurities present in waste water are called contaminant. This waste water is called sewage.
SOURCE OF WASTE WATER
Domestic Waste Water :
It includes all kinds of wastes like human excreta, food waste, soaps, detergents, oil, animal excreta, urine, etc.
Agricultural Waste Water :
The waste water generated from farms and agricultural fields contains harmful pesticides, weedicides and animal wastes.
Industrial Waste Water :
The waste water generated from various industries contains harmful chemicals. The discharge of industrial waste water is called Industrial effluent.
Petroleum Oil :
The leakage of petroleum oil into the sea during drilling and shipping pollutes sea water. Oil spill is caused due to release of oil into rivers and oceans knowingly or unknowingly.
Mining :
Waste water is also generated as a result of mining activities.
Construction Activity :
Lot of waste water is generated during various stages of building houses, homes, malls, multiplexes, etc.
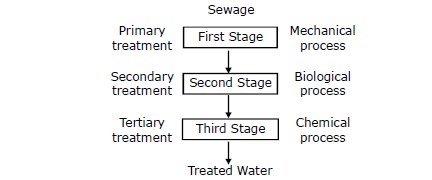
SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANT
There are three processes which are involved in treating waste water before it is discharged into the water reservoirs. These processes are :
1. Primary treatment
2.Secondary treatment
3. Tertiary treatment
Primary Treatment :
* It is the first stage and is called primary treatment. The waste water is passed through rotating screens to remove large objects.
* The water is then passed through a grit and sand tank to remove small stones and pebbles.
* The soild wastes such as faeces settle down at the bottom of the tank and are removed with the help of a scraper. This is a sludge
* The sludge can be used for production of biogas to be used as fuel or for producing electricity. Light materials float on top and are known as scum. The scum is removed with the help of a skimmer.
Secondary Treatment :
* It is the second stage and is called secondary treatment. The treatment at this stage involves pumping of air into the clarified water to help aerobic bacteria to grow. The bacteria decompose the suspended waste.
* The activity of the bacteria produces decomposed organic material which settle down at the bottom of the tank as activated sludge. It is passed through sand drying beds to separate the solid material out of it. This solid waste can be used as manure.
Tertiary Treatment :
* It is the third stage and is called tertiary treatment . The treated water now undergoes chemical treatment.
* The water is disinfected with chemicals like chlorine or may be exposed to ultraviolet rays to kill disease-causing organisms.
* It can also be treated with ozone gas. The water is then discharged into the distribution system. A schematic diagram of a waste water treatment plant is shown in
USES OF TREATED WATER
The treated water which is obtained from sewage treatment plant is used for irrigating fields, lawns and for aquaculture. In Kolkata the treated water is used for fisheries and growing crops and vegetables. The treated water is finally released in streams and rivers.
HOW WE CAN REDUCE SEWAGE GENERATION
* Leakage in sewer lines should be cheked and repaired regularly.
* Use flushes with low capacity to reduce flushed water.
* Waste water from basins, sinks and washing machines can be used again for watering plants or wiping floors
* Never pour household products such as cooking oil, fat, butter, plastic, etc. down the drain. These materials can block the pipes and sewage may start overflowing in your home or at public places.
* Newer throw paints, solvents, insecticides, automobile oils, and medicines down the drain as they may kill microbes that help to purify water.
* Used tea leaves, solid food remains, sanitary towels, toys, etc. should not be thrown in the waste water pipe because these materials may choke the drains
* Ask civic authorities to cover the open drains of your area.
* Plant eucalyptus trees all along sewage ponds as these plants absorb surplus water rapidly.
WASTE WATER AND DIESEASE
Drinking of waste & contaminated water cause many human disease in India
People consuming contaminated water may suffer from diseases like gastroenteritis, dysentry, typhoid, cholera, meningitis and hepatitis.
Olympiad Problems NCERT Class 7 Waste Water Management
Question. Waste water containing human excreta is known as –
(A) Sewage
(B) Sewer
(C) Sewerage
(D) None
Answer
A
Question. Discharge of industrial waste is called –
(A) Effluent
(B) Sewer
(C) Sewerage
(D) Sludge
Answer
A
Question. The light materials which float during waste water treatment is –
(A) Sludge
(B) Scum
(C) Biogas
(D) Sewer
Answer
B
Question. Water is disinfected by –
(A) Chlorine
(B) Ozone
(C) UV-radiations
(D) All of these
Answer
D
Question. Primary treatment is a –
(A) Mechanical process
(B) Chemical process
(C) Biological process
(D) None of these
Answer
A
Question. The discharge of industrial waste water is called-
(A) Industrial effluents
(B) Oil spill
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Answer
A
Question. Sewage is often processed with the help of –
(A) Septic tank
(B) Over tank
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Answer
C
Question. Contaminated water disease is –
(A) Gastroenteritis
(B) Malaria
(C) Flu
(D) None of these
Answer
D
Question. A feul produced by anaerobic fermentation of sludge is –
(A) Biogas
(B) Petrol
(C) Kerosene
(D) Wood
Answer
A
MCQs for NCERT Class 7 Science Waste Water Management
Question. Which of the following is not an ancient water harvesting structure?
(A) kattas
(B) sargam
(C) kulhs
(D) surangams
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following is not a natural resource?
(A) soil
(B) water
(C) electricity
(D) natural gas
Answer
C
Question. The three R’s which can help us to conserve natural resources for long term use are
(A) recycle, regenerate, reuse
(B) reduce, regenerate, reuse
(C) reduce, reuse, redistribute
(D) reduce, recycle, reuse
Answer
D
Question. The main reason for the abundant coliform bacteria in the water of river Ganga is
(A) immersion of ashes of the dead into the river
(B) washing of clothes on the banks of river
(C) discharge of industrial wastes into river water
(D) disposal of unburnt corpses into river water
Answer
D
Question. The pH of a sample of water collected from a river is found to be in the range of 3.5 to 4.5 The most likely reason for this is the waste being discharged into the river from a
(A) soap and detergent manfacturing factory
(B) car battery manufacturing factory
(C) alcohol manufacturing factory
(D) plastic cups moulding factory
Answer
B
Question. Ground water will not be depleted due to
(A) process of afforestation
(B) establishing thermal power plants
(C) process of deforestation
(D) cultivation of high yielding varieties of crops
Answer
A
Question. Ahars, kattas, Bhundhis and Khadins are the modes of
(A) grain storage
(B) soil conservation
(C) water harvesting
(D) cold storage
Answer
C
Question. Khadins are used in Rajasthan to
(A) hold water for irrigation
(B) recharge groundwater
(C) promote soil erosion
(D) trap wild animals
Answer
B
Question. If excessive amounts of hot water are discharged into a lake, the immediate result will most likely be –
(A) an increase in the sewage content of the lake
(B) an increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen in the lake
(C) an increase in the amount of PCB pollution in the lake
(D) a decrease in the amount of phosphates in the lake
Answer
B
Question. All of earth’s water, land and atmosphere, within which life exists is known as
(A) a population
(B) a community
(C) a biome
(D) the biosphere
Answer
D
Question. What is the main source of water pollution in India?
(A) Municipal sewage
(B) Bathing
(C) Industrial discharge
(D) Both A and C
Answer
D
Question. What minerals are found in the run-off from agricultureal land and untreated sewage effluents that are responsible for eutrophication of water bodies?
(A) Phosphorous and carbon
(B) Nitrogen and phosphorus
(C) Potassium and arsenic
(D) Iron and manganese
Answer
B
Question. Which sector is the single-largest consumer of fresh water in India?
(A) Agriculture
(B) Industry
(C) Domestic
(D) Power
Answer
A
Question. Water harvesting is
(A) collection of river water
(B) collection of rainwater in storage tanks or in the soil to recharge ground water
(C) harvesting of water from tube wells
(D) all of the above
Answer
B
Question. What is the origin of energy that drives the water cycle?
(A) Tress
(B) Water
(C) Mountains
(D) Sun
Answer
D
Question. Which of the following is not found in polluted water?
(A) Blue green algae
(B) Larvae of stone fly
(C) Water hyacinth
(D) Sewage fungi
Answer
B
Question. Which of the following processes is involved in the water cycle?
(A) Evaporation, hibernation and dehydration
(B) Evaporation, condensation and precipitation
(C) Paddling, swimming and drinking
(D) Bathing, sunning and drinking
Answer
B
Question. Water that moves over the surface of the ground into lakes and rivers is called
(A) ground water
(B) a water table
(C) run-off
(D) the water cycle
Answer
C
Question. Waste that can be broken down by bacteria
(A) biological
(B) biochemical
(C) biodegradable
(D) chemical
Answer
A
Question. Disinfection of water is done by
(A) chlorine
(B) ozone
(C) UV radiation
(D) all of these
Answer
A
Question. Sewage is a kind of
(A) agricultural waste
(B) liquid waste
(C) mining waste
(D) gaseous waste
Answer
B
Question. Wastewater generated from houses is commonly called
(A) sludge
(B) sewage
(C) effluent
(D) none of the above
Answer
B
Question. Stage of wastewater treatment of removing large particles
(A) disinfection
(B) secondary
(C) primary
(D) chlorination
Answer
C
Question. Malaria can be triggered by
(A) open drains
(B) closed drains
(C) taps
(D) pipelines
Answer
A
Question. The disease caused by polluted water
(A) jaundice
(B) dysentery
(C) cholera
(D) all of these
Answer
D

We hope the above Waste Water Management Class 7 Science are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science


